Slip joint
A slip joint allows for axial (through telescopic action) and torsional movement between adjacent pipes (due to thermal expansion or contraction). The joint itself can be fixed using an anchor if so designed. Slip joints are susceptible to lateral buckling due to internal pressure, and may become less effective when subjected to small bending loads. Proper guiding to prevent buckling and keeping the two telescopic parts concentric are therefore necessary.
Since the primary purpose of a slip joint is to absorb axial growth, the joint is ideal for placing it towards the end of long pipe runs, while its growth is directed axially by the use of one or more guides.
A Slip Joint is input by typing “s” under the Type column or by selecting “Slip joint” from the Element types dialog.
The Slip joint dialog is shown.
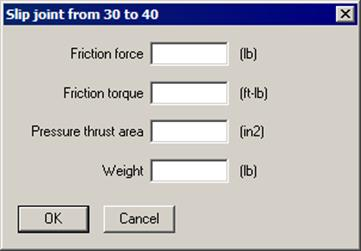
A slip joint manufacturer should be able to provide you the required data for a slip joint.
A slip joint will have axial deflection or rotation only when the external forces exceed the friction force or friction torque respectively. If the pressure thrust area is input, CAEPIPE imposes a thrust load of: Pressure x Thrust area on both nodes of the slip joint. The weight is the empty weight of the joint. The contents, insulation and additional weight are added to the empty weight. A slip joint is considered to be rigid in lateral directions in CAEPIPE.
Weight of the slip joint is input in lbf or kgf and NOT its mass. Whenever mass is required for a calculation as in the case of forming Mass matrix for dynamic analysis, or in calculating inertia force as (mass x acceleration) for static seismic analysis, CAEPIPE internally computes the mass to be equal to (weight / g-value).
Example:
Assume that we want to model a (telescoping action) slip joint that allows only axial movement with no torsion. The outer sleeve of the joint is anchored to hold it in place while the other end is free to translate axially. The axial (friction) force has to exceed 1,100 lb. (you will need to get this datum from a manufacturer’s catalog) to make the slip joint move and the slip joint cannot rotate about the axial direction. So, the data would look similar to that shown next between nodes 30 and 40.
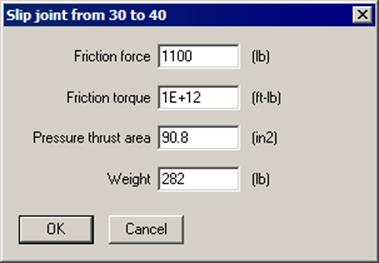
And, the modeling on the layout screen would look thus:
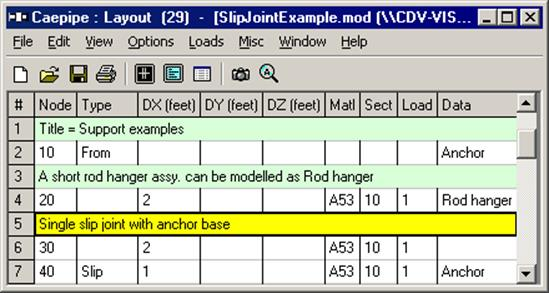
See the topic on Nonlinearities for related information.